Quick Answer: When comparing a generator vs battery backup, the right emergency backup power option depends on your needs. Generators provide high wattage for whole-home use but require fuel and maintenance. Battery and solar systems deliver silent, instant, zero-emission power ideal for families prioritizing safety, reliability, and long-term independence.
The power’s out, the lights are gone, and you’re left deciding how to keep everything running. Should you trust a gas generator, invest in a battery system, or go solar? Being familiar with generator vs. battery backup options is key when planning for real emergencies.
With outages lasting longer and happening more often, choosing the right emergency backup power options is essential for keeping your home safe, your food cold, and your family connected when the grid goes down.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Power Output and Capacity Comparisons for Emergency Scenarios
- Startup Time and Reliability During Disasters
- Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Operation
- Safety Considerations and Environmental Impact
- Maintenance Requirements and System Longevity
- Best Applications for Each Power Solution
- Sizing Your Backup Power for Family Needs
- Installation Complexity and Home Integration
- Making the Right Choice for Your Preparedness Level
- Choosing the Right Emergency Backup Power Options
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Sources
Key Takeaways
- Backup power systems like generators, batteries, and solar options provide different strengths for emergency preparedness.
- A typical family of four needs 3,000Wh per day during an outage, or about 9,000Wh for 72-hour coverage.
- Generators offer high power output but consume fuel quickly and require frequent maintenance.
- Battery systems deliver instant, silent power without emissions, making them ideal for homes with medical devices or children.
- Solar integration with battery storage allows for indefinite off-grid power during extended outages.
- Battery and solar systems last up to 25 years with minimal maintenance and no fuel storage risks.
- Shop tested, reliable backup solutions at Batten Shop to protect your home and family during any power emergency.
Power Output and Capacity Comparisons for Emergency Scenarios
When the grid fails, the key question is simple: how much power do you really need? A typical family of four uses around 30 kWh per day under normal conditions, but during an outage, you can reduce that to 3-5 kWh daily by running only essentials:
- Refrigerator: 1,500 Wh/day
- LED Lights: 200 Wh/day
- Phone Charging: 50 Wh/day
- Fan or Small Heater: 1,000 Wh/day
Batten Emergency focuses on tested, verifiable specs so you know exactly what to expect when it counts.
Your Power Pain Points
Families face three common issues when planning for outages:
- Medical Device Reliability: Devices like CPAP machines need continuous power, and not all systems can sustain that load.
- Noise and Visibility: Generators can reach 85 dB and attract unwanted attention, while batteries run silently.
- Fuel Storage and Safety: Keeping large amounts of gasoline is risky and impractical for long-term readiness.
Batten Shop curates equipment designed for real emergency use, not just outdoor recreation.
Generator Power Capabilities
Gas generators still dominate raw power output, producing 5,000-12,000 watts continuously. A 7,500-watt model can handle refrigerators, lights, and even small air conditioners at once.
The tradeoff is fuel consumption: at full load, you’ll burn 12-18 gallons per day, requiring over 50 gallons for a three-day outage. That fuel must be stored, rotated, and kept safe – no small task during extended events.
Battery Backup Systems
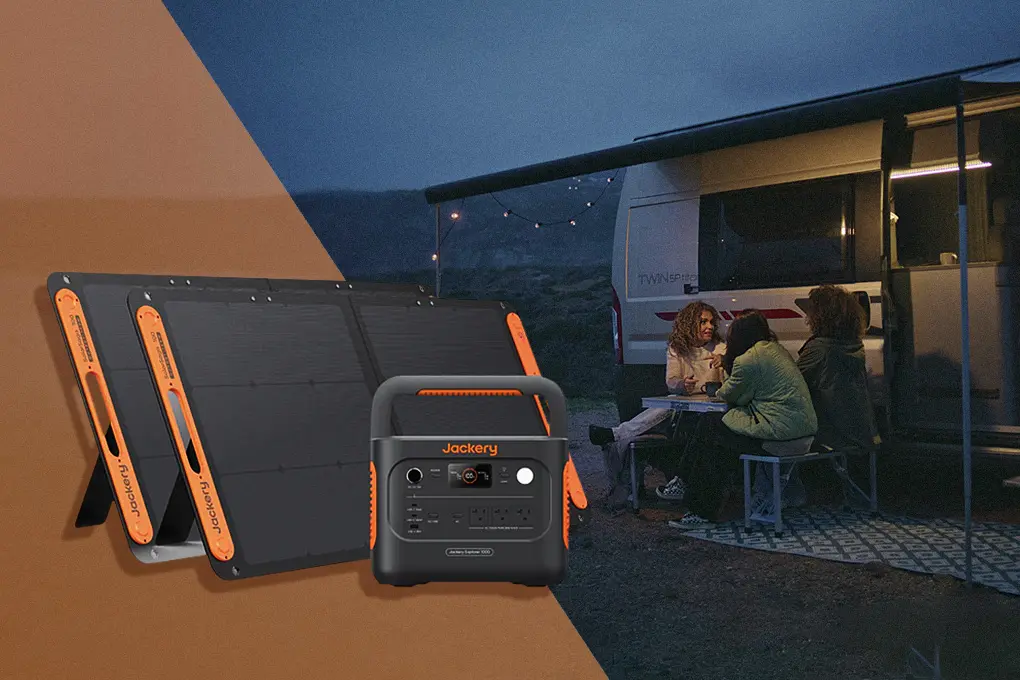
Modern battery systems range from 500 Wh portables to 5,000 Wh home units. The Jackery Explorer 5000 Plus offers 5,040 Wh capacity and 7,200 W output, enough to power essentials like a refrigerator for two days or charge devices for several.

Batteries deliver power instantly, operate quietly, and require no fuel or maintenance.
For most homes, a properly sized battery system provides silent, dependable energy for critical needs – making it the practical choice for families who want low-maintenance emergency power without the complications of fuel storage or generator upkeep.
Emergency Runtime Comparison
| Power Source | Capacity | Runtime for Essentials | Days of Emergency Coverage | Recharge/Refuel Time |
| 7,500W Gas Generator | 6 gal tank | 8-10 hours per tank | Unlimited with fuel | 5 minutes to refuel |
| 3,000Wh Battery Station | 3,000Wh | 18-24 hours | 1.5-2 days | 4-6 hours (AC), 8 hours (solar) |
| 5,000Wh Battery + 400W Solar | 5,000Wh | 30-40 hours | 3-5 days (indefinite with sun) | Continuous with sunlight |
| 10kW Natural Gas Generator | Pipeline | Continuous | Unlimited | No refueling needed |
| 2,000Wh Portable Station | 2,000Wh | 12-16 hours | 1 day | 2-3 hours (AC), 5 hours (solar) |
Pairing solar panels with a battery system changes how long you can operate off-grid. A 400W solar array typically produces 1,600-2,000 Wh per day, even under mild winter sunlight. When paired with a 5 kWh battery, this setup can sustain essential household loads indefinitely by balancing generation with consumption.
Larger systems – such as a 10 kWh battery with 800W of solar input – can easily support lighting, refrigeration, and communication devices for extended periods without dropping below half charge. This combination offers genuine energy independence, eliminating dependence on fuel supplies or grid access.
Batten Shop’s power generation collection includes solar-compatible systems selected for reliability, scalability, and long-term emergency performance – ideal for families or preppers who want lasting, self-sufficient power during extended outages.

Startup Time and Reliability During Disasters
When a storm knocks out power in the middle of the night, every second counts. Battery backup systems switch to power in under 20 milliseconds, fast enough that digital clocks and electronics don’t even flicker.
Units available through Batten Shop include automatic transfer switches that detect outages instantly.
That means your refrigerator keeps running, your CPAP machine stays powered, and your security system never drops offline. Instant response eliminates the late-night scramble to get lights or life-supporting devices back on.
The Reliability Problem with Generators
A major issue few generator sellers mention is that around one in three portable generators fail to start during real emergencies. Common causes include stale fuel, gummed carburetors, drained starter batteries, or water contamination – issues that build up quietly over time.
You may maintain your unit faithfully, yet still find yourself yanking a starter cord in the dark while food spoils and sump pumps stall.
Battery systems don’t have those weak points. They operate silently, require no fuel, and can last 10 years or more with minimal upkeep.
Standby generators equipped with automatic transfer switches start within 10-30 seconds, while portable models can take 5-15 minutes to set up under ideal conditions. In heavy rain or snow, setup times stretch far longer, especially when cords and switches need manual handling.
Maintenance and Environmental Factors
Reliability is also about how each system performs over time. Gas generators require oil changes every 50-100 hours, periodic spark plug replacements, and carburetor cleaning after storage. Many users find their generators won’t start after months of inactivity due to clogged fuel systems.
Battery systems, by contrast, need only to stay charged above 20% capacity, and solar panels – which have no moving parts – come with 25-year performance warranties and near-zero maintenance needs.
Weather also plays a key role. Gas generators often struggle in sub-20°F temperatures, requiring special oil or pre-warming to start. Batteries lose about 20% of capacity at 0°F but still function reliably. Solar panels actually perform better in cold weather, though shorter winter days reduce total output.
In short, when reliability and response time matter most, battery and solar systems offer dependable power when fuel-based options can’t.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Operation
The sticker price tells only part of the story – and this is where most families make expensive mistakes. A quality 7,500-watt portable generator costs $1,200-$2,500, while installation of a 10kW standby generator runs $5,000-$8,000 including the transfer switch.
But factor in fuel costs: at $3.50 per gallon, running that portable generator 8 hours daily costs $42-$63. Over 20 years of occasional use (100 hours annually), you’ll spend $7,000-$10,500 on gasoline alone. The frustration of constantly buying fuel that might go bad before you use it drives many preppers to battery solutions.
Breaking Down the Real Economics
Battery systems require higher upfront investment, triggering immediate sticker shock. A 3,000Wh portable power station costs $2,500-$3,500, while whole-home systems start at $10,000.
Add solar panels ($1,500 for 400W) and you’re looking at $4,000-$5,000 for a basic solar generator setup.
However, Batten Shop’s curated selection focuses on the sweet spot: systems powerful enough for real emergencies but affordable enough for prep-curious families. The power generation collection includes options starting under $1,000 that can keep critical devices running for 24-48 hours.
Total Cost Analysis
| System Type | Initial Cost | 10-Year Operating Cost | Cost Per Day of Backup | Maintenance Requirements |
| 7,500W Portable Generator | $1,500 | $5,000 (fuel) + $500 (maintenance) | $18.50 | Oil changes, filters, winterization |
| 10kW Standby Generator | $7,000 | $3,000 (natural gas) + $1,000 (service) | $11.00 | Annual service, battery replacement |
| 3,000Wh Battery Station | $3,000 | $200 (electricity) | $3.30 | Minimal, keep charged |
| 5kWh Battery + 400W Solar | $5,500 | $0 (solar powered) | $1.50 | Panel cleaning, battery cycling |
| Hybrid Battery/Generator | $4,500 | $1,500 (occasional fuel) | $6.00 | Both systems’ maintenance |
Families experiencing frequent outages (monthly or more) find battery systems pay for themselves within 5-7 years through eliminated fuel costs.
Tax incentives further improve battery/solar economics. The federal tax credit covers 30% of battery costs when installed with solar through December 2025. Many states offer additional rebates – California’s SGIP program provides up to $1,000/kWh for battery storage. Generators receive no federal incentives and limited state support.
Safety Considerations and Environmental Impact
Carbon monoxide is the most dangerous aspect of generator use. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) reports 85-100 generator-related CO deaths each year, with hundreds more hospitalizations.
During Hurricane Irma (2017), 16 people died from generator CO poisoning – more than from the storm itself. These numbers highlight why Batten Emergency prioritizes zero-emission battery systems that eliminate this risk entirely.
Hidden Safety and Security Risks
Generators bring more than CO danger. Running at 70-85 decibels, they are as loud as a garbage disposal and can alert neighbors during power outages or civil unrest.
Many HOAs ban nighttime generator use, leaving families vulnerable when outages last overnight. Battery backup systems solve both problems – they run silently, produce no fumes, and can safely power indoor spaces, making them ideal for apartments and suburban homes.
Fire and Fuel Hazards
Traditional generators require storing large amounts of gasoline, often 20-50 gallons, which poses major fire risks during wildfires or long-term storage. Gasoline starts degrading within 30 days without stabilizer, increasing the likelihood of failure or ignition.
Modern LiFePO₄ battery systems are non-flammable, thermally stable, and can withstand punctures or high heat without catching fire. With 6,000+ life cycles, they provide a decade of reliable power without the hazards of fuel storage or combustion.
Environmental Impact and Noise
Generators burn roughly 0.75 gallons of fuel per hour per kilowatt, producing about 20 pounds of CO₂ per gallon. Running an 8 kW generator for a week releases over 2,500 pounds of emissions, the equivalent of driving 3,000 miles.
Battery and solar systems are completely emission-free and operate quietly, with only a faint inverter hum under 30 decibels. In normal use, they even offset grid power, cutting your household carbon footprint year-round.
For families prioritizing safety, reliability, and environmental responsibility, battery and solar systems offer clean, silent, and worry-free power – without the noise, fumes, or risks that come with fuel-based generators.
Maintenance Requirements and System Longevity
Regular upkeep determines how long your backup power system will last when the grid goes down.
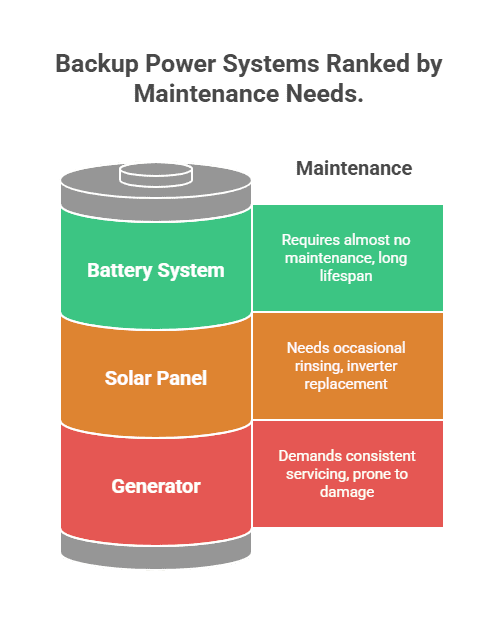
Generator Maintenance
Generators demand consistent servicing. Portable units need oil changes every 50 hours, air filter cleaning every 100 hours, and spark plug replacement yearly. Standby models require professional maintenance once a year, typically costing $200-$400. Ethanol fuel can damage carburetors within months, and pests often chew through wiring in idle units – common causes of failure during outages.
Battery System Maintenance
Battery systems require almost no maintenance. Keep charge levels between 20-80%, store them at room temperature, and cycle monthly if unused. Built-in management systems prevent overcharging and heat damage. After 10 years, most retain 70-80% capacity, still delivering reliable power.
Solar Panel Care
Solar panels are nearly maintenance-free. Rain removes most debris, though dusty climates may need quarterly rinsing. Inverters last 10-15 years before replacement, usually costing $1,000-$2,000. The Jackery solar panels we’ve tested show no degradation after three years of daily use.
System Lifespan Comparison
- Portable Generators: 2,000-3,000 hours (about 10 years)
- Standby Generators: 10,000+ hours with servicing
- Battery Stations: 3,000-6,000 cycles or 10-15 years
- Solar Panels: 25-year warranties, maintaining 80%+ efficiency after 30 years
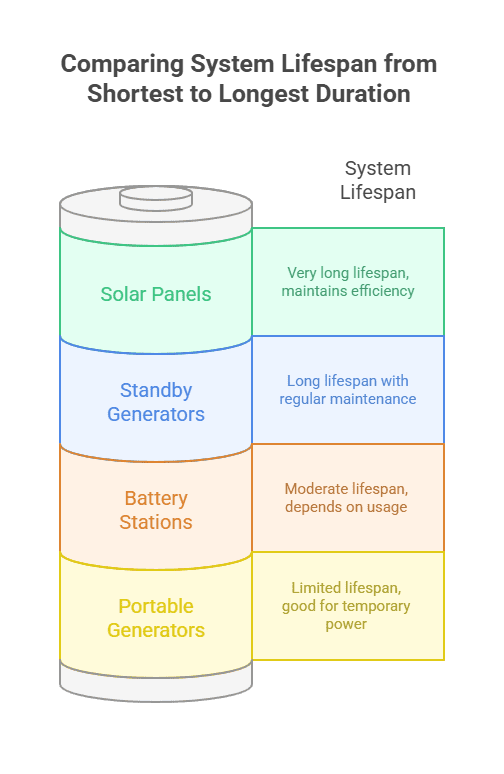
Battery and solar systems offer the longest lifespan with the least upkeep – ideal for consistent, low-maintenance emergency power.
Best Applications for Each Power Solution
Each backup power option has strengths depending on where you live, how much power you need, and how long you plan to sustain it.
When Generators Make Sense
Generators work best for high-demand power situations where noise and emissions are not concerns. They’re ideal for rural properties, workshops using 240V tools, and whole-home backup during extended outages.
They also suit construction sites and RV setups where fuel access and noise tolerance are expected. For regions with steady fuel supply and minimal neighbors, generators still deliver the most watts per dollar.
That said, they require regular maintenance and mechanical know-how, making them better suited for experienced users comfortable with small-engine upkeep.
Battery Stations for Urban and Suburban Use
Battery stations are the safest and most practical solution for urban and suburban households. They’re silent, emission-free, and ideal for apartments, condos, and homes with medical needs such as CPAP machines or oxygen concentrators.
Because they operate instantly and quietly, they’re also valuable during civil unrest, when keeping a low profile matters. Portable units from Batten Shop offer true mobility for evacuations – something no 200-pound generator and 50 gallons of fuel can match.
Solar Combinations for Energy Independence
Solar and battery systems provide long-term energy independence for off-grid homes, RVs, and boats. They excel in regions with frequent power outages or disasters that limit fuel supply.
Once installed, solar panels keep batteries charged indefinitely, providing sustainable, renewable energy without maintenance headaches.
For long-term preppers or those concerned about grid instability or EMP events, storing extra charge controllers and inverters in a Faraday cage ensures your system remains operational for decades.
Important Features
| Feature | Gas Generator | Battery Station | Solar System | Best For Emergency Scenario |
| Instant Power | No (10-30 seconds) | Yes (<20ms) | Yes (if battery included) | Medical devices, security systems |
| Silent Operation | No (70-85 dB) | Yes | Yes | Urban areas, nighttime use |
| Indoor Safe | Never | Yes | Yes (battery only) | Apartments, severe weather |
| Fuel Required | Yes (gas/propane/NG) | No (grid charging) | No (sun charging) | Long-term outages, remote locations |
| Portable | Some models | Most models | Limited | Evacuation, camping, travel |
| Weather Resistant | Yes | Limited | Panels yes, batteries no | Outdoor installation |
| Maintenance | High | Minimal | Minimal | Set-and-forget reliability |
| Power Output | Highest (5-20kW) | Moderate (1-5kW) | Variable (0.2-10kW) | Whole-house vs. essentials |
| Runtime | Unlimited with fuel | 6-48 hours | Unlimited with sun | Extended emergencies |
| Initial Cost | Low-Moderate | Moderate-High | High | Budget constraints |
Sizing Your Backup Power for Family Needs
Properly sizing your backup system starts with identifying what truly matters during an outage. Many families either overspend on oversized systems or underestimate their real power needs, leaving essentials offline. For a 72-hour emergency, focus on:
- Refrigeration (prevents $500+ food loss)
- Lighting (for safety and morale)
- Communication Devices (for emergency updates)
- Climate Control (for extreme temperatures)
A typical family of four requires around 3,000Wh per day, or 9,000Wh total for 72-hour preparedness. To simplify planning, Batten Shop offers pre-configured backup bundles sized for common household scenarios.
Medical Equipment and Critical Loads
If your family relies on medical devices, backup power becomes a necessity, not a luxury.
- CPAP machines use 30-60W (about 240-480Wh per night)
- Oxygen concentrators draw 300-600W continuously
- Powered wheelchairs consume 2,000-4,000Wh per charge
These devices require battery systems that switch power instantly. Generator startup delays of even 30 seconds can be life-threatening. Batten Emergency’s medical-grade battery systems are tested to deliver uninterrupted power for these exact scenarios.
Household Vulnerabilities to Consider
Every home has unique needs. Families with infants may need reliable power for bottle warmers or formula preparation (about 500Wh daily). Homes with elderly residents require steady heating or cooling (2,000-3,000Wh daily during extremes).
Pet owners, especially with aquariums or reptiles, should account for temperature control (300-500Wh daily). Review your emergency kit carefully – many power-dependent essentials are easy to overlook.
Keeping Food and Medicine Cold
Cold storage is critical in long outages. A standard refrigerator uses 1,000-1,500Wh daily, while chest freezers average 600-800Wh.
These appliances run 8-10 hours per day during outages if you keep doors closed. To extend cooling time, freeze water bottles before storms – they act as thermal mass to maintain cold temperatures longer and provide emergency drinking water as they thaw.
Installation Complexity and Home Integration
Each power system comes with different setup requirements that affect cost, safety, and usability during emergencies.
Portable Generator Setup
Portable generators appear simple but require careful installation for safety. Using multiple extension cords is inefficient and risky. A transfer switch – costing $500-$800 – is essential to prevent dangerous backfeed into utility lines.
Most municipalities also require permits and professional installation, typically adding $1,000-$2,000. Without a transfer switch, generators can only power plug-in devices, leaving out critical systems like furnaces, sump pumps, and well pumps.
Standby Generator Installation
Standby generators are fully automated but come with higher installation demands. The process involves concrete pad placement, gas line connections, and automatic transfer switch installation, all of which must meet local electrical and building codes.
Installation costs often match or exceed the unit’s purchase price. Natural gas units require utility coordination, while propane setups need tanks placed according to setback rules – limitations that can exclude many urban or suburban homes.
Battery Station Integration
Battery backup systems are the easiest to set up. Portable units are plug-and-play, powering devices through standard outlets or extension cords immediately.
For larger setups, a critical loads panel (about $2,000-$3,000 installed) can route backup power to key household circuits like refrigerators, routers, and medical equipment.
Smart panels such as Span or Lumin manage load distribution automatically, shedding non-essential circuits to extend battery runtime.
Adding Solar Capability
Solar integration increases complexity but remains manageable. Portable panels connect directly to battery stations through MC4 connectors, while ground-mounted or roof systems may require electrical permits and professional help.
Making the Right Choice for Your Preparedness Level
Choosing the right system depends on your living situation, risk tolerance, and budget.
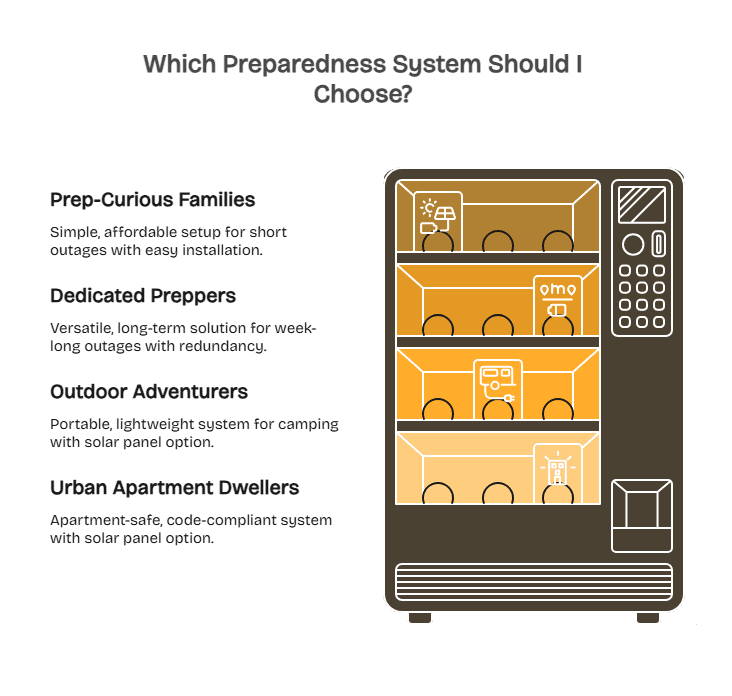
Prep-Curious Families
If you’re new to preparedness, start small and simple. A 2,000Wh portable battery station ($1,500-$2,000) from Batten Shop powers essentials for 24 hours and charges via wall or vehicle outlets – no installation required. Add a 100W solar panel ($300) to extend runtime. This setup easily covers short outages while you plan for future upgrades. Pair it with shelf-stable emergency food to minimize cooking power needs.
Dedicated Preppers
For week-long outages, a hybrid system combining a 5,000Wh battery and a 2,000W inverter generator offers the best balance of safety and redundancy. Use the battery for quiet daily operation and run the generator only for high loads or battery recharging. Expect to invest $4,000-$5,000 for a versatile, long-term solution that keeps power flowing even if one system fails.
Outdoor Adventurers
For campers or overlanders, portability is key. A 1,500Wh battery station (under 35 lbs) powers your base camp for a weekend and fits easily in most vehicles. Add 200W folding solar panels for unlimited backcountry power. These same systems double as home backups, giving you a solution you’ll use and maintain year-round.
Urban Apartment Dwellers
Apartment residents can’t use generators, making battery systems the only option. A 3,000Wh portable battery runs essentials for 48-72 hours and stores neatly in a closet. Consider window-mounted solar panels (where permitted) or energy-efficient appliances to stretch runtime. Batten Shop curates apartment-safe, code-compliant systems ideal for urban living and HOA restrictions.
Choosing the Right Emergency Backup Power Options
Choosing between a generator, battery system, or solar setup comes down to balancing power, safety, and simplicity. Generators still dominate high-load performance but bring ongoing costs, noise, and maintenance challenges.
Battery systems deliver instant, quiet power for critical loads with minimal upkeep, while solar integration extends runtime indefinitely.
For most homes, combining a well-sized battery station with optional solar panels offers the most dependable and sustainable preparedness strategy. When every minute and watt count, investing in a reliable backup power solution from Batten Shop ensures your family stays safe, connected, and comfortable through any outage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Run My Entire House on a Battery Backup System During an Extended Outage?
Yes, but it requires substantial investment. A whole-home battery system needs 20-30kWh capacity costing $15,000-$25,000. Most families find powering essential circuits only (refrigerator, lights, outlets) with a 10kWh system more practical. Check our extended power outage preparation guide for load management strategies.
How Long Will a Generator Run on 5 Gallons of Gas During an Emergency?
A 5,000-watt generator at 50% load burns approximately 0.5 gallons per hour, giving you 10 hours runtime on 5 gallons. Efficiency varies significantly – newer inverter generators achieve 14-18 hours from 5 gallons at quarter load. Store enough fuel for 72 hours minimum using proper fuel storage techniques. Remember that gasoline degrades within 30 days without stabilizer, creating an ongoing maintenance burden that battery solutions from Batten Shop eliminate entirely.
What Size Battery Do I Need to Run My Refrigerator for 3 Days Without Power?
A standard refrigerator consuming 1,500Wh daily needs 4,500Wh total for 72 hours. However, refrigerators cycle on/off, and you’ll want margin for other devices. A 5,000Wh battery station provides comfortable coverage. For maximum efficiency, investigate blackout food safety techniques to minimize door openings and extend runtime.
Can I Connect a Portable Generator Directly to My House Electrical Panel?
Never connect a generator directly without a proper transfer switch – this creates deadly backfeed risk that can kill utility workers. Manual transfer switches cost $500-$800 plus installation. Interlock kits offer a code-legal alternative for $150-$300. Battery systems available at Batten Shop often include safe transfer switches or plug-and-play connections, eliminating this complex installation requirement that stops many families from implementing backup power.
How Do I Prevent My Backup Power System From Being Stolen During Civil Unrest?
Secure generators with heavy chains and locks to permanent structures. Many preppers build locking enclosures or store units in garages, running exhaust outside safely. Battery systems stay indoors, eliminating theft risk. Consider emergency gear theft protection strategies including security cameras powered by your backup system.
Do Battery Backup Systems Work With Well Pumps During Power Outages?
Most 240V well pumps require 3,000-5,000 watts starting surge, challenging for battery systems. Some newer variable-speed pumps work with large battery inverters. Alternatively, install a 120V transfer pump drawing from your well for emergency water access. Traditional generators handle well pumps easily, making them preferable for rural properties dependent on well water.
Sources
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 2025, Federal Tax Credits for Energy Efficiency. Federal Tax Credits for Energy Efficiency | ENERGY STAR
- California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), 2025, Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP). Self-Generation Incentive Program
- United States Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), 2025, Carbon Monoxide Safety Education. Carbon Monoxide | CPSC.gov
- UL Standards & Engagement (ULSE), 2024, Mitigating the Risks of CO Poisoning from Portable Generators Mitigating the Risks of CO Poisoning from Portable Generators – UL Standards & Engagement




